在 JVM 平台中用 JUnit 测试代码——教程
This tutorial shows you how to write a simple unit test in a Kotlin/JVM project and run it with the Gradle build tool.
In this project, you'll use the kotlin.test library and run the test using JUnit.
If you're working on a multiplatform app, see the Kotlin Multiplatform tutorial.
To get started, first download and install the latest version of IntelliJ IDEA.
Add dependencies
Open a Kotlin project in IntelliJ IDEA. If you don't have a project, create one.
Open the
build.gradle(.kts)file and check that thetestImplementationdependency is present. This dependency allows you to work withkotlin.testandJUnit:
【Kotlin】
dependencies {
// Other dependencies.
testImplementation(kotlin("test"))
}
【Groovy】
dependencies {
// Other dependencies.
testImplementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-test'
}
- Add the
testtask to thebuild.gradle(.kts)file:
【Kotlin】
tasks.test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
【Groovy】
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
If you use the
useJUnitPlatform()function in your build script, thekotlin-testlibrary automatically includes JUnit 5 as a dependency. This setup enables access to all JUnit 5 APIs, along with thekotlin-testAPI, in JVM-only projects and JVM tests of Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) projects.
Here's a complete code for the build.gradle.kts:
plugins {
kotlin("jvm") version "2.1.21"
}
group = "org.example"
version = "1.0-SNAPSHOT"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testImplementation(kotlin("test"))
}
tasks.test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
Add the code to test it
Open the
Main.ktfile insrc/main/kotlin.The
srcdirectory contains Kotlin source files and resources. TheMain.ktfile contains sample code that printsHello, World!.Create the
Sampleclass with thesum()function that adds two integers together:class Sample() { fun sum(a: Int, b: Int): Int { return a + b } }
Create a test
In IntelliJ IDEA, select Code | Generate | Test... for the
Sampleclass: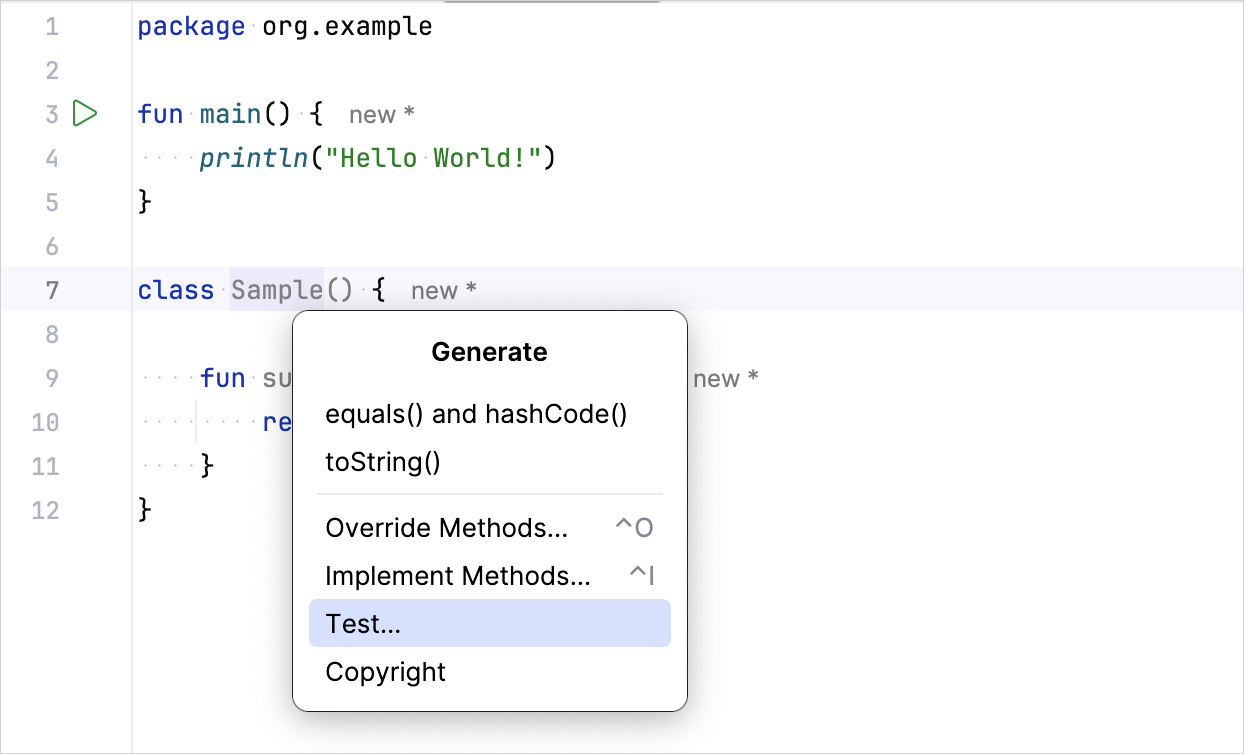
Specify the name of the test class. For example,
SampleTest: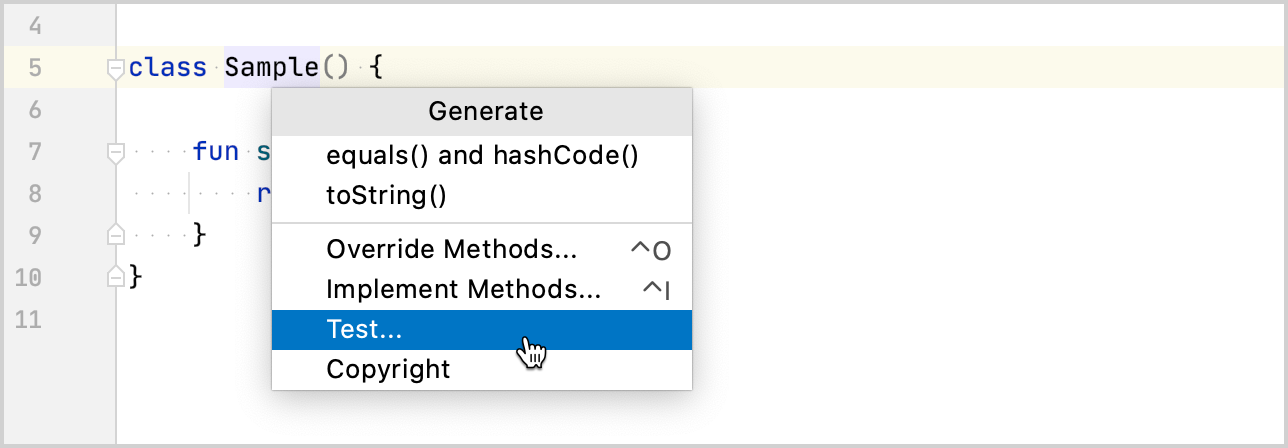
IntelliJ IDEA creates the
SampleTest.ktfile in thetestdirectory. This directory contains Kotlin test source files and resources.You can also manually create a
*.ktfile for tests insrc/test/kotlin.Add the test code for the
sum()function inSampleTest.kt:- Define the test
testSum()function using the@Testannotation. - Check that the
sum()function returns the expected value by using theassertEquals()function.
import org.example.Sample import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.* import kotlin.test.Test class SampleTest { private val testSample: Sample = Sample() @Test fun testSum() { val expected = 42 assertEquals(expected, testSample.sum(40, 2)) } }- Define the test
Run a test
Run the test using the gutter icon:

You can also run all project tests via the command-line interface using the
./gradlew checkcommand.Check the result in the Run tool window:
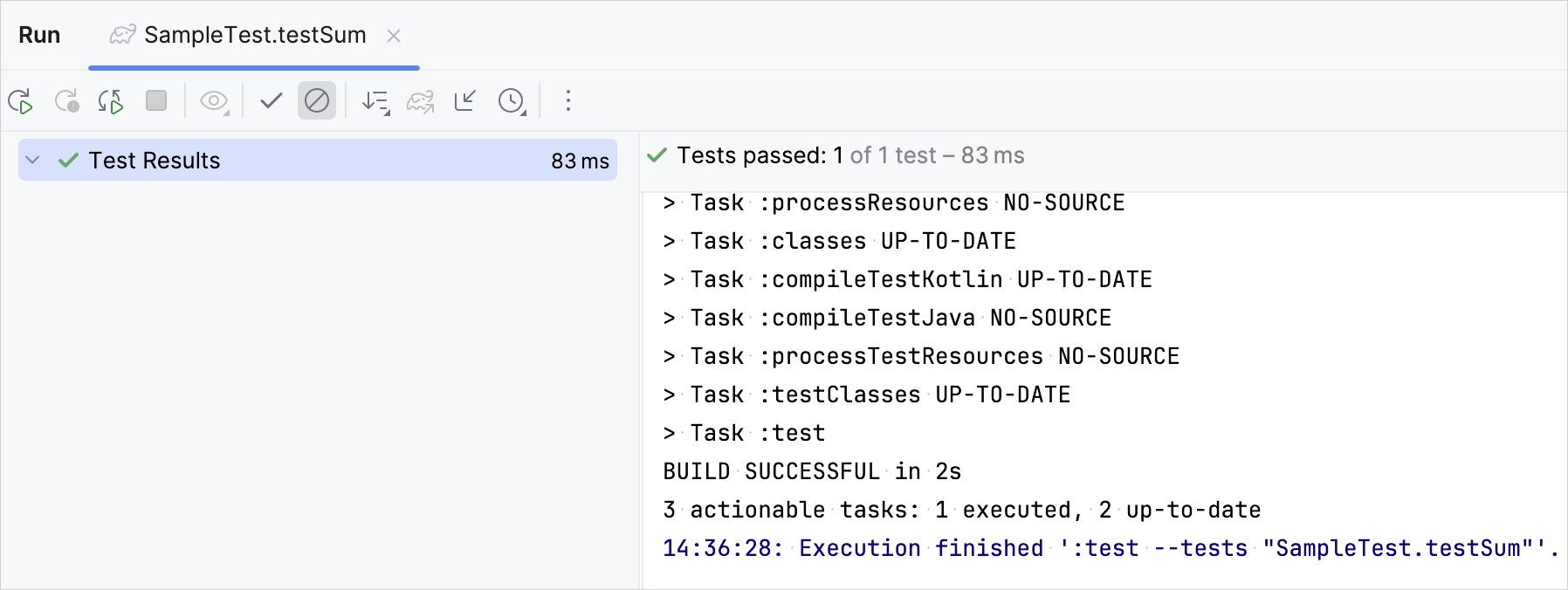
The test function was executed successfully.
Make sure that the test works correctly by changing the
expectedvariable value to 43:@Test fun testSum() { val expected = 43 assertEquals(expected, classForTesting.sum(40, 2)) }Run the test again and check the result:
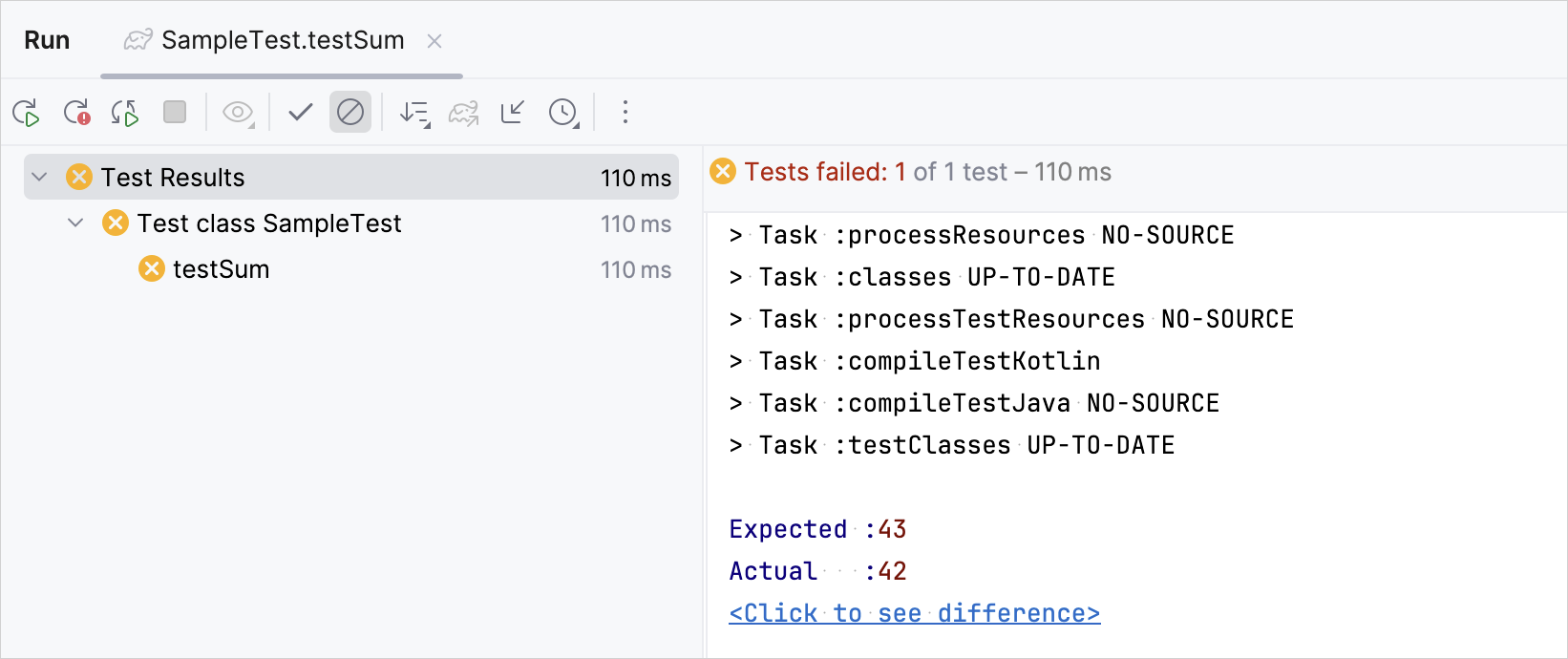
The test execution failed.
下一步做什么
Once you've finished your first test, you can:
- Write more tests using other
kotlin.testfunctions. For example, use theassertNotEquals()function. - Improve your test output with the Kotlin Power-assert compiler plugin. The plugin enriches the test output with contextual information.
- Create your first server-side application with Kotlin and Spring Boot.