创建第一个跨平台应用
This is the second part of the Getting started with Kotlin Multiplatform for mobile tutorial. Before proceeding, make sure you've completed the previous step.
Set up an environment
Create your first cross-platform app
Update the user interface
Add dependencies
Share more logic
Wrap up your project
Here you will learn how to create and run your first Kotlin Multiplatform application using Android Studio.
Create the project from a template
- In Android Studio, select File | New | New Project.
Select Kotlin Multiplatform App in the list of project templates, and click Next.

Specify a name for your first application, and click Next.
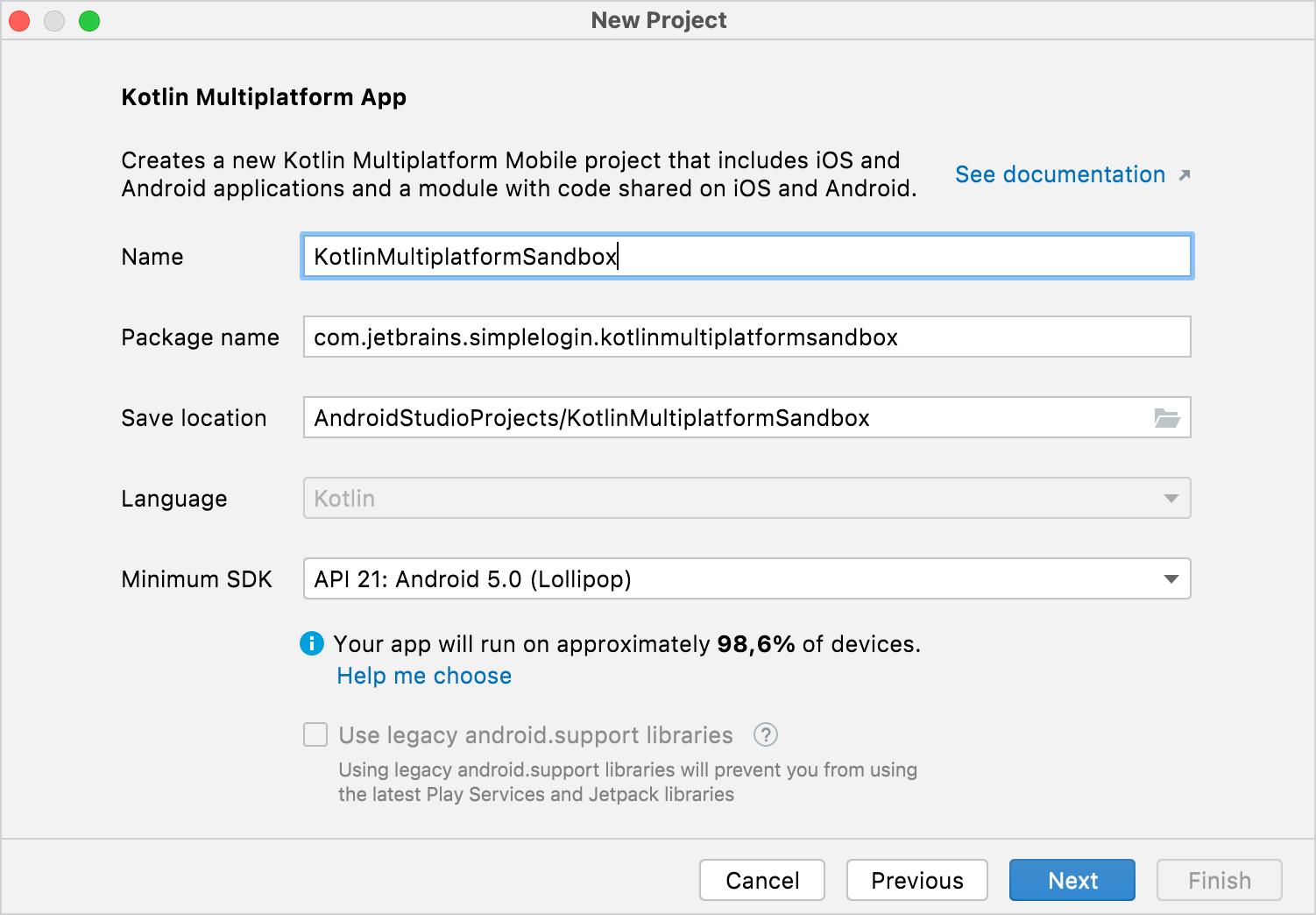
In the iOS framework distribution list, select the Regular framework option.

We recommend using the regular framework for your first project, as this option doesn't require third-party tools and has fewer installation issues.
For more complex projects, you might need the CocoaPods dependency manager that helps handle library dependencies. To learn more about CocoaPods and how to set up an environment for them, see CocoaPods overview and setup.
Keep the default names for the application and shared folders. Click Finish.
The project will be set up automatically. It may take some time to download and set up the required components when you do this for the first time.
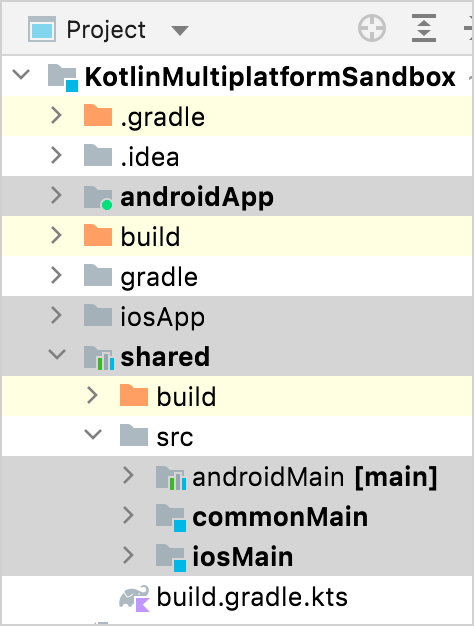
Examine the project structure
To view the full structure of your mobile multiplatform project, switch the view from Android to Project.

Each Kotlin Multiplatform project includes three modules:
- shared is a Kotlin module that contains the logic common for both Android and iOS applications – the code you share between platforms. It uses Gradle as the build system that helps you automate your build process.
- androidApp is a Kotlin module that builds into an Android application. It uses Gradle as the build system. The androidApp module depends on and uses the shared module as a regular Android library.
- iosApp is an Xcode project that builds into an iOS application. It depends on and uses the shared module as an iOS framework. The shared module can be used as a regular framework or as a CocoaPods dependency, based on what you've chosen in the previous step in iOS framework distribution. In this tutorial, it's a regular framework dependency.

The shared module consists of three source sets: androidMain, commonMain, and iosMain. Source set is a Gradle
concept for a number of files logically grouped together where each group has its own dependencies.
In Kotlin Multiplatform, different source sets in a shared module can target different platforms.
The common source set uses the common Kotlin code, and platform source sets use Kotlin flavors:
Kotlin/JVM for androidMain and Kotlin/Native for iosMain.
When the shared module is built into an Android library, common Kotlin code gets treated as Kotlin/JVM. When it is built into an iOS framework, common Kotlin gets treated as Kotlin/Native:

Write common declarations
The common source set contains shared code that can be used across multiple target platforms. It's designed to contain code that is platform-independent. If you try to use platform-specific APIs in the common source set, IDE will show a warning:
Open the
Greeting.ktfile and try to access one of the Java classes,java.util.Random().nextBoolean(), inside thegreet()function:import java.util.Random fun greet(): String { val firstWord = if (Random().nextBoolean()) "Hi!" else "Hello!" }Android Studio highlights that
Randomclass is unresolved because you can't call specific Java functions from the common Kotlin code.- Follow IDE's suggestions and replace it with
kotlin.random.Randomfrom the Kotlin standard library. This is a multiplatform library that works on all platforms and is included automatically as a dependency. The code should now compile successfully. Add a bit of unpredictability to the greeting. Update the shared code with the
reversed()function from the Kotlin standard library for reversing the text:import kotlin.random.Random class Greeting { private val platform: Platform = getPlatform() fun greet(): String { val firstWord = if (Random.nextBoolean()) "Hi!" else "Hello!" return "$firstWord\nGuess what it is! > ${platform.name.reversed()}!" } }
Writing the code only in common Kotlin has obvious limitations because it can't use any platform specifics. Using interfaces and the expect/actual mechanism solves this.
Add platform-specific implementations
The common source set can define an interface or an expected declaration. Then each platform source sets,
in this case androidMain and iosMain, has to provide actual platform-specific implementations for the expected
declarations from the common source set.
While generating the code for a specific platform, the Kotlin compiler merges expected and actual declarations and generates a single declaration with actual implementations.
When creating a project in Android Studio, you get a template with the
Platform.ktfile in thecommonMainmodule:interface Platform { val name: String }It's a common
Platforminterface with information about the platform.Switch between the
androidMainand theiosMainmodules. You'll see that they have different implementations of the same functionality for the Android and the iOS source sets:// Platform.kt in androidMain module: import android.os.Build class AndroidPlatform: Platform { override val name: String = "Android ${Build.VERSION.SDK_INT}" }// Platform.kt in the iosMain module: import platform.UIKit.UIDevice class IOSPlatform: Platform { override val name: String = UIDevice.currentDevice.systemName() + " " + UIDevice.currentDevice.systemVersion }- The
nameproperty implementation fromAndroidPlatformuses the Android platform code, namely theandroid.os.Builddependency. This code is written in Kotlin/JVM. If you try to accessjava.util.Randomhere, this code will compile. - The
nameproperty implementation fromIOSPlatformuses iOS platform code, namely theplatform.UIKit.UIDevicedependency. It's written in Kotlin/Native, meaning you can write iOS code in Kotlin. This code becomes a part of the iOS framework, which you will later call from Swift in your iOS application.
- The
Check the
getPlatform()function in different source sets. Its expected declaration doesn't have a body, and actual implementations are provided in the platform code:// Platform.kt in commonMain module: expect fun getPlatform(): Platform// Platform.kt in androidMain module: actual fun getPlatform(): Platform = AndroidPlatform()// Platform.kt in iosMain module: actual fun getPlatform(): Platform = IOSPlatform()
Here, the common source set defines an expected getPlatform() function and has actual implementations,
AndroidPlatform() for the Android app and IOSPlatform() for the iOS app, in the platform source sets.
While generating the code for a specific platform, the Kotlin compiler merges expected and actual declarations
into a single getPlatform() function with its actual implementations.
That's why expected and actual declarations should be defined in the same package − they are merged into one declaration
in the resulting platform code. Any invocation of the expected getPlatform() function in the generated platform code
calls a correct actual implementation.
Now you can run the apps to ensure everything works.
Explore the expect/actual mechanism (optional)
The template project uses the expect/actual mechanism for functions but the same works for most Kotlin declarations, such as properties and classes. Let's implement an expected property:
Open
Platform.ktin thecommonMainmodule and add the following at the end of the file:expect val num: IntThe Kotlin compiler complains that this property has no corresponding actual declarations in the platform modules.
Try to provide the implementation right away with:
expect val num: Int = 42You'll get an error saying that expected declarations must not have a body, in this case an initializer. The implementations must be provided in actual platform modules. Remove the initializer.
Select the
numproperty. Press Option + Enter and choose "Create actual property for module ModuleName.shared.main (JVM)". IDE generates the actual property inandroidMain/Platform.kt. You can then complete the implementation:actual val num: Int = 1Now provide the implementation for the
iosMainmodule. Add the following toiosMain/Platform.kt:actual val num: Int = 2Add the
numproperty to thegreet()function to see the differences:fun greet(): String { val firstWord = if (Random.nextBoolean()) "Hi!" else "Hello!" return "$firstWord [$num]\nGuess what it is! > ${platform.name.reversed()}!" }
Run your application
You can run your multiplatform application for both Android or iOS from Android Studio.
Run your application on Android
- Create an Android virtual device.
- In the list of run configurations, select androidApp.
Choose your Android virtual device and click Run.


Run on a different Android simulated device
Learn how to configure the Android Emulator and run your application on a different simulated device.
Run on a real Android device
Learn how to configure and connect a hardware device and run your application on it.
Run your application on iOS
- Launch Xcode in a separate window. The first time you may also need to accept its license terms and allow it to perform some necessary initial tasks.
In Android Studio, select iosApp in the list of run configurations and click Run.
If you don't have an available iOS configuration in the list, add a new iOS simulated device.


Run on a new iOS simulated device
If you want to run your application on a simulated device, you can add a new run configuration.
In the list of run configurations, click Edit Configurations.
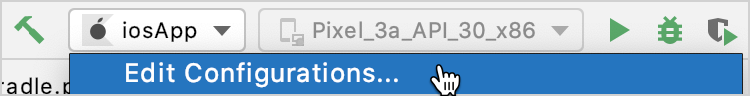
Click the + button above the list of configurations and select iOS Application.

Name your configuration.
Select the Xcode project file. For that, navigate to your project, for example KotlinMultiplatformSandbox, open the
iosAppfolder and select the.xcodeprojfile.In the Execution target list, select a simulated device and click OK.

Click Run to run your application on the new simulated device.
Run on a real iOS device
- Connect a real iPhone device to Xcode.
- Make sure to code sign your app. For more information, see the official Apple documentation.
- Create a run configuration by selecting an iPhone in the Execution target list.
- Click Run to run your application on the iPhone device.
If your build fails, follow the workaround described in this issue.
Next step
In the next part of the tutorial, you'll learn how to update the UI elements using platform-specific libaries.
See also
- See how to create and run multiplatform tests to check that the code works correctly.
- Learn more about the project structure, the shared module's artifacts, and how the Android and iOS apps are produced.
Get help
- Kotlin Slack. Get an invite and join the #multiplatform channel.
- Kotlin issue tracker. Report a new issue.