在本地 Swift 包中使用 Kotlin
* You have an iOS app with local SPM modules. * You've already set up a Kotlin Multiplatform project targeting iOS on your local machine. * Your existing iOS project has a static linking type.
[Choose the integration method that suits you best](multiplatform-ios-integration-overview.md)
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to integrate a Kotlin framework from a Kotlin Multiplatform project into a local package using the Swift package manager (SPM).
To set up the integration, you'll add a special script that uses the embedAndSignAppleFrameworkForXcode Gradle task
as a pre-action in your project's build settings. To see the changes made in common code reflected in your Xcode project,
you'll only need to rebuild the Kotlin Multiplatform project.
This way, you can easily use Kotlin code in local Swift packages, compared to a regular direct integration method, that adds the script to the build phase and requires rebuilding both the Kotlin Multiplatform and the iOS project to get the changes from the common code.
If you aren't familiar with Kotlin Multiplatform, learn how to set up the environment and create a cross-platform application from scratch first.
{style="tip"}
Set up the project
The feature is available starting with Kotlin 2.0.0.
To check the Kotlin version, navigate to the
build.gradle(.kts)file in the root of your Kotlin Multiplatform project. You'll see the current version in theplugins {}block at the top of the file.Alternatively, check the version catalog in the
gradle/libs.versions.tomlfile.{style="tip"}
The tutorial assumes that your project is using direct integration
approach with the embedAndSignAppleFrameworkForXcode task in the project's build phase. If you're connecting a Kotlin
framework through CocoaPods plugin or through Swift package with binaryTarget, migrate first.
Migrate from SPM binaryTarget integration
To migrate from the SPM integration with binaryTarget:
- In Xcode, clean build directories using Product | Clean Build Folder or with the
Cmd + Shift + K shortcut. - In every
Package.swiftfile, remove both dependencies to the package with a Kotlin framework inside and target dependencies to the products.
Migrate from the CocoaPods plugin
If you have dependencies on other Pods in the
cocoapods {}block, you have to resort to the CocoaPods integration approach. Currently, it's impossible to both have dependencies on Pods and on the Kotlin framework in a multimodal SPM project.{style="warning"}
To migrate from the CocoaPods plugin:
- In Xcode, clean build directories using Product | Clean Build Folder or with the
Cmd + Shift + K shortcut. In the directory with Podfile, run the following command:
pod deintegrateRemove the
cocoapods {}block from yourbuild.gradle(.kts)files.- Delete the
.podspecfile and the Podfile.
Connect the framework to your project
The integration into
swift buildis currently not supported.{style="note"}
To be able to use Kotlin code in a local Swift package, connect the Kotlin framework generated from the multiplatform project to your Xcode project:
In Xcode, go to Product | Scheme | Edit scheme or click the scheme icon in the top bar and select Edit scheme:
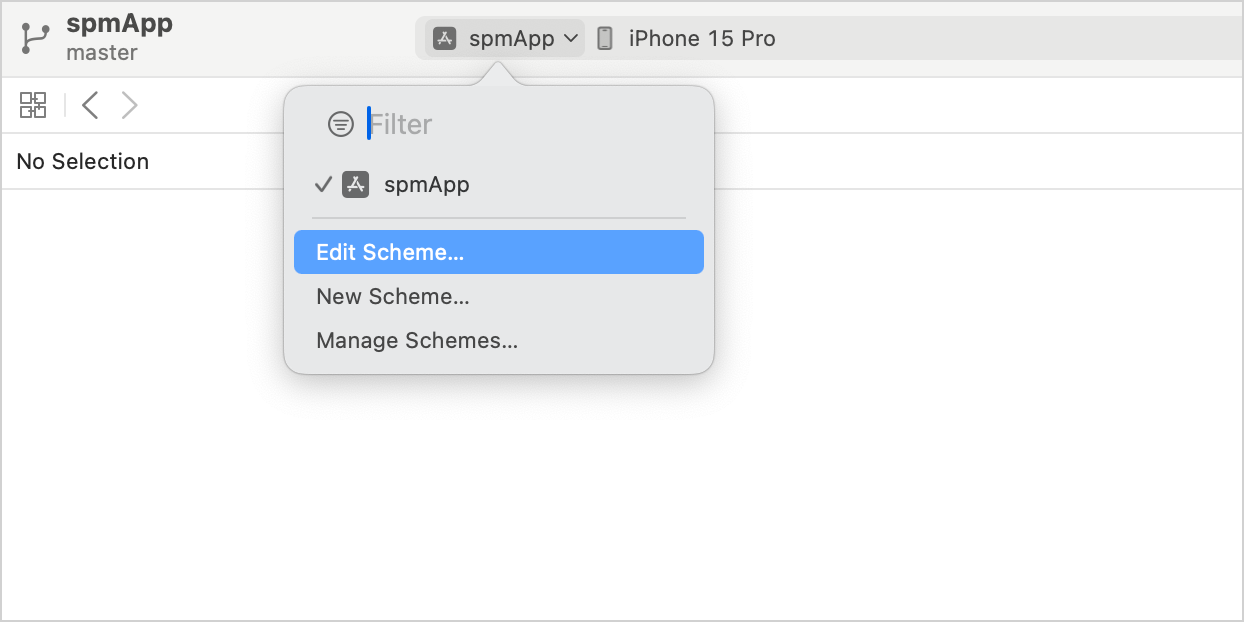
Select the Build | Pre-actions item, then click + | New Run Script Action:

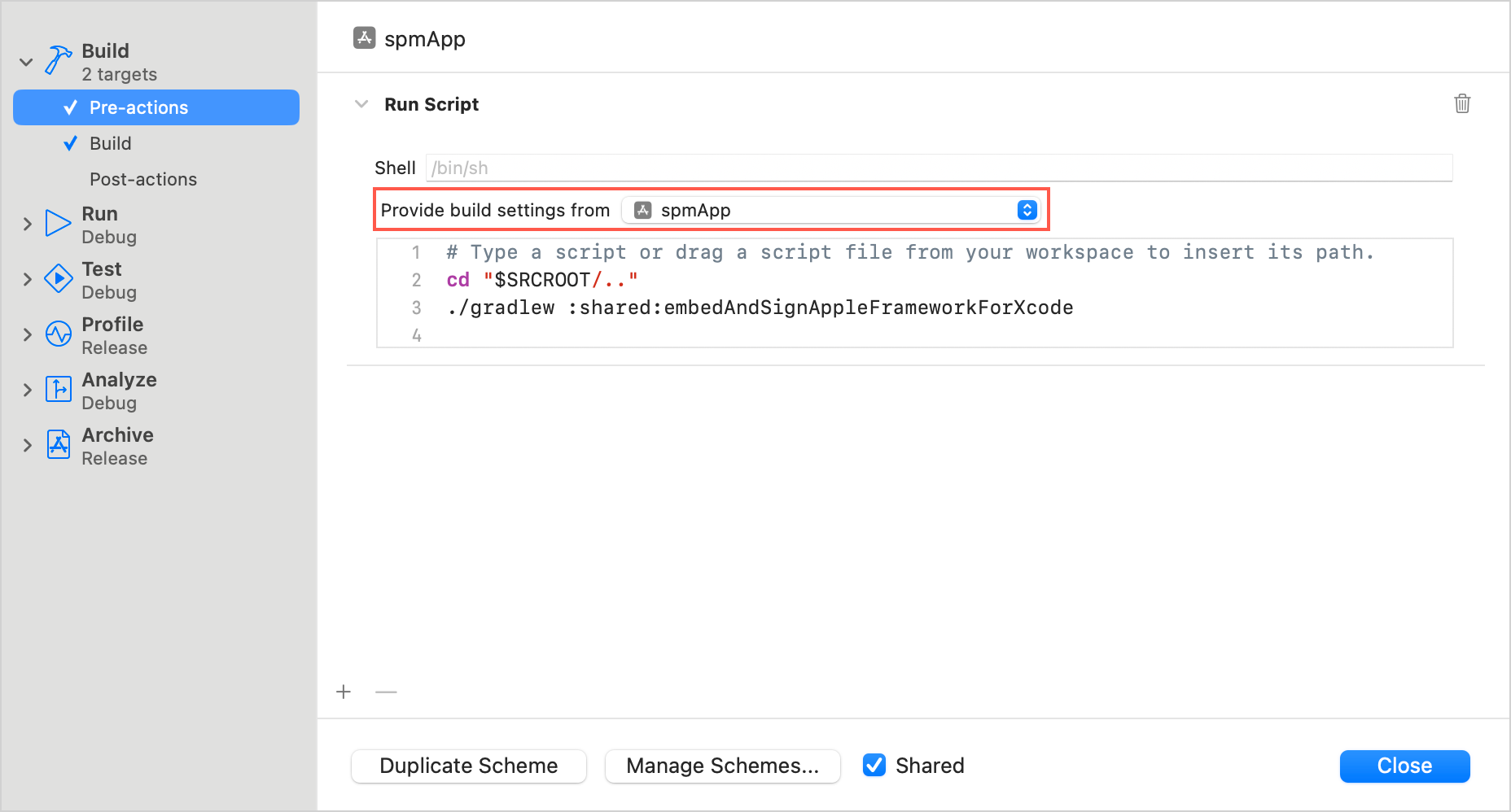
Adjust the following script and add it as an action:
cd "" ./gradlew : :embedAndSignAppleFrameworkForXcode - In the
cdcommand, specify the path to the root of your Kotlin Multiplatform project, for example,$SRCROOT/... - In the
./gradlewcommand, specify the name of the shared module, for example,:sharedor:composeApp.
- In the
Choose your app's target in the Provide build settings from section:
You can now import the shared module into your local Swift package and use Kotlin code.
In Xcode, navigate to your local Swift package and define a function with a module import, for example:
import Shared public func greetingsFromSpmLocalPackage() -> String { return Greeting.greet() }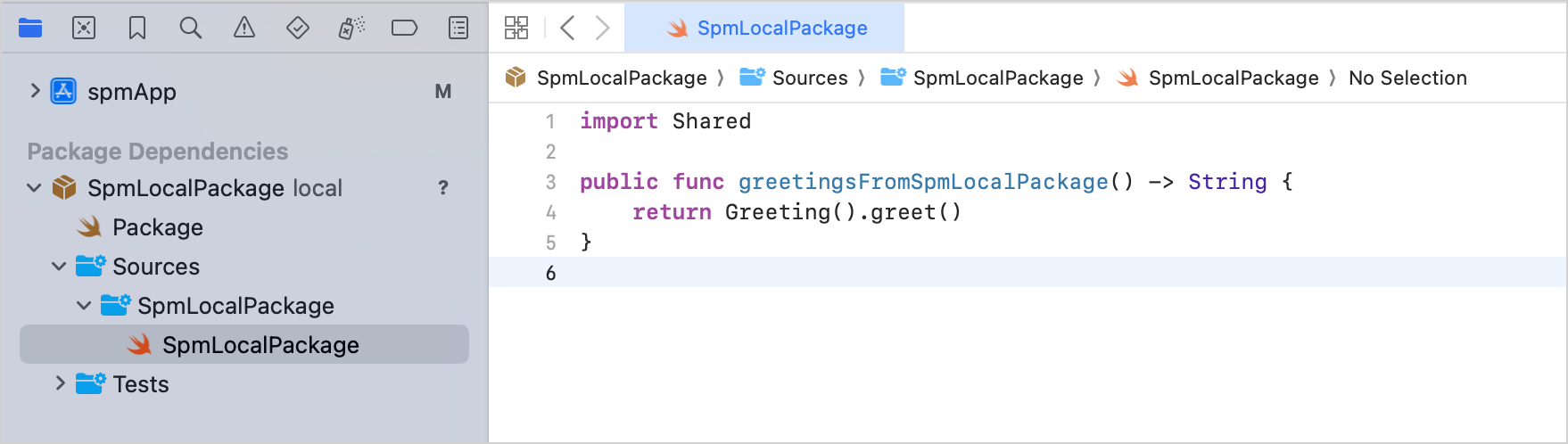
In the
ContentView.swiftfile of your iOS project, you can now use this function by importing the local package:import SwiftUI import SpmLocalPackage struct ContentView: View { var body: some View { Vstack { Image(systemName: "globe") .imageScale(.large) .foregroundStyle(.tint) Text(greetingsFromSpmLocalPackage()) } .padding() } } #Preview { ContentView() }Build the project in Xcode. If everything is set up correctly, the project build will be successful.
There are a couple more factors worth considering:
- If you have a custom build configuration that is different from the default
DebugorRelease, on the Build Settings tab, add theKOTLIN_FRAMEWORK_BUILD_TYPEsetting under User-Defined and set it toDebugorRelease. - If you encounter an error with script sandboxing, open the iOS project settings by double-clicking the project name, then on the Build Settings tab, disable the User Script Sandboxing under Build Options.
